
At Lupin, we believe that economic advancement and environmental preservation can go hand-in-hand, as they are interconnected. Safeguarding natural resources is crucial for the overall well-being of humanity and the growth of business. As a manufacturer of medications that save lives, we recognize the importance of protecting the environment, which includes enabling access to clean air and water.
In all regions of our operations across, we prioritize the environment by surpassing regulations and norms. Together, with our employees, partners, and local communities we strive to establish sustainable practices that safeguard the environment and enhance the long-term value of our business.
of Incinerable Hazardous Waste Generated is sent for pre-processing / co-processing
Reduction in absolute GHG emissions (Scope 1 and 2)
Water Positivity
MtCO2e YoY Reduction by shifting to Ocean from Air in Downstream Transport (Scope 3)
Share of Renewable Energy Across Operations
of water used in India operations is recycled
Sites are Zero- Liquid Discharge
Certification for 3 Facilities under process

Lupin prioritizes responsibility toward the environment, health, safety, and sustainability (EHS&S). We have an established EHS&S policy guiding our environmental governance systems, emphasizing efficient resource use, pollution prevention, energy conservation, water recycling, waste reduction, and emission minimization. The Board of Directors oversee the policy implementation, while the senior management and the ESG core committee ensure daily adherence. Our commitment extends throughout the value chain, including suppliers and contractors, with globally aligned and top-tier environmental and safety standards expected from all Lupin business partners. This policy also applies to all products and services.
We understand that achieving strong environmental performance requires more than just policy development and implementation. Hence, we have designed a series of monitoring and review systems to ensure ongoing compliance with environmental regulations.
Currently, we are in the process of implementing ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 at our manufacturing sites in Goa, Nagpur, and Indore. Our plan is to extend these certifications to all our other Indian sites, including research and development facilities, by FY24.
We regularly monitor our EHS&S practices and performance and communicate the findings through a comprehensive report. This report is reinforced by a thorough EMS audit of our systems and processes, ensuring that we meet regulatory standards. During bi-yearly meetings, our Board of Directors review the performance report and audit findings. These meetings also enable discussions around critical aspects of our EHS&S performance and identify gaps in our environmental performance. From there, we work to address these gaps and continuously improve our environmental performance and management system.
We actively engage with all our stakeholders to educate them about effective environmental management. We do this through yearly training and awareness sessions. These training are targeted towards ensuring that the key aspects and expectations of our EHS&S policy are adhered to. In FY23, we conducted 738,266 hours of training to cover all our employees and contractors.
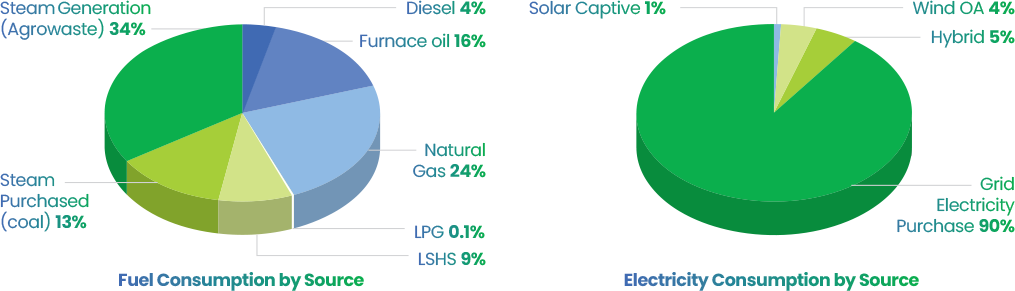
We prioritize responsible and efficient energy consumption across our operations. Our sustainability strategy centers around this goal, and we continually invest in new technologies, systems, and processes to improve our energy consumption practices. Our four-year energy consumption trend and a detailed breakup are provided below.



We are committed to achieving higher energy efficiency and have successfully implemented various technologies and measures to increase energy efficiency across all our sites. We regularly track the progress of our energy-efficient measures across all thirteen manufacturing locations in India and three overseas locations including Brazil, Mexico, and the U.S.
Our efforts include replacing old conventional luminaries with energy-efficient LED lights, replacement of conventional AC motors with DC electronically commutated motors in AHUs, refrigeration plant optimization, pumping optimization, boiler & utility equipment efficiency improvements, which has resulted in significant energy efficiency improvement and power cost reduction.
Despite the national pledges made since COP26, it is evident that these efforts are not enough to reduce predicted 2030 emissions significantly, nor are they sufficient to achieve the Paris Agreement goal of limiting global warming to well below 2°C. As things stand, current policies indicate a 2.8°C temperature rise by the end of the century. This highlights the urgent need for swift and comprehensive measures to mitigate GHG emissions across organizations. We recognize the gravity of the situation and are accelerating our efforts to achieve ambitious decarbonization targets.
To help achieve this goal, we are implementing process and product efficiency measures, increasing the use of renewable energy at our operating locations, and procuring green energy from the grid. Furthermore, we are implementing energy efficiency initiatives at our sites to reduce our carbon footprint.
We have embarked on a comprehensive transition to cloud technology, aiming to shift away from physical storage and server options. As part of this move, we have successfully implemented Microsoft Cloud Based Technologies across our various sites and offices. By leveraging these technologies, we have achieved operational efficiency and significantly reduced our carbon emissions. We use the Microsoft Emissions Impact Dashboard to quantify and track our progress, which enables us to accurately measure the emissions savings resulting from migrating our production workloads to the cloud.
In FY23, our collective efforts translated into a reduction of approximately 27 tCO2e across our operations. This achievement underscores our commitment to sustainable practices and paves the way for our gradual transition toward a fully cloud-based setup.
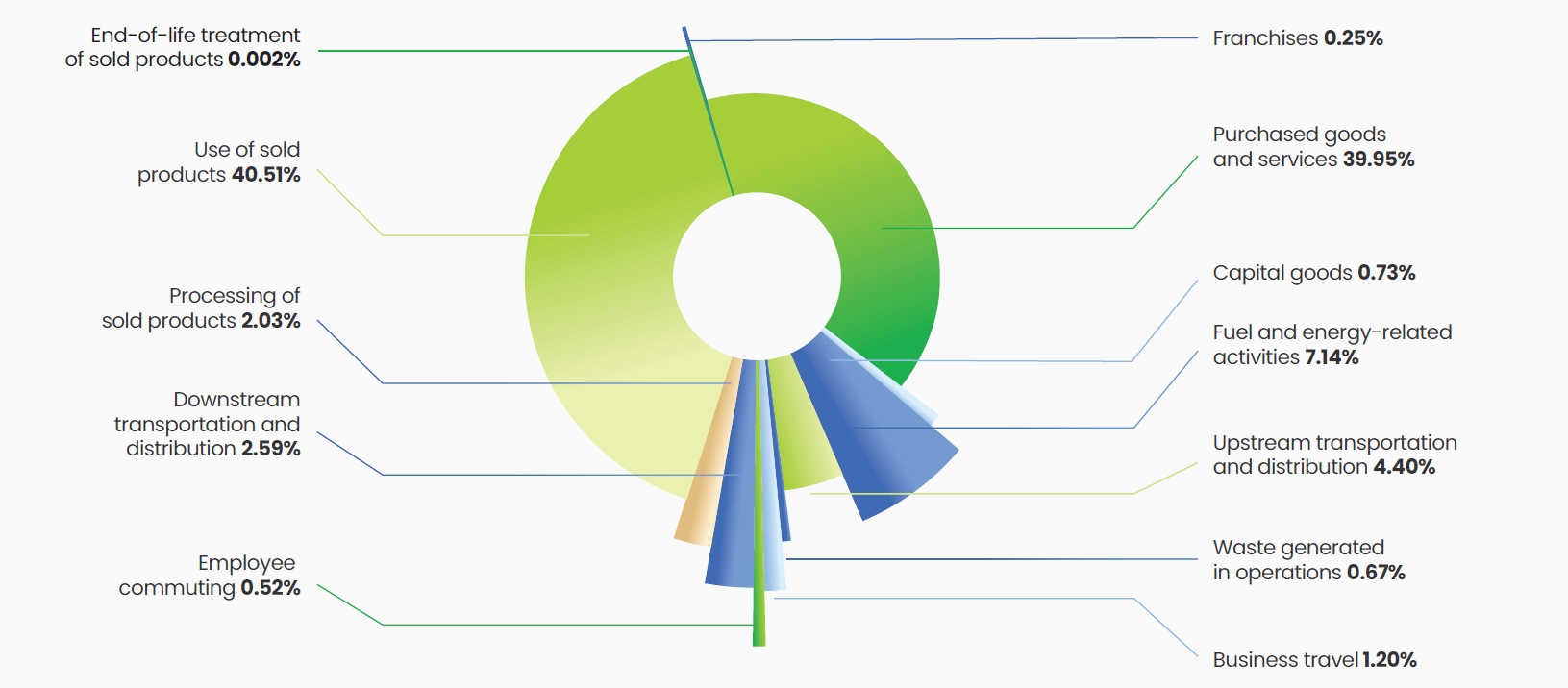
As an organization committed to sustainability, we recognize the significance of Scope 3 emissions in our total emissions. Our comprehensive Scope 3 assessment in FY23 enabled an improved understanding of our greenhouse gas emissions across our value chain and beyond.
As part of this assessment, we engaged with multiple stakeholders internally and across our value chain to calculate Scope 3 emissions for eight categories. The categories shortlisted for our Scope 3 assessment include Purchased Goods and Services, Capital Goods, Fuel and Energy, Waste Generated and Disposed, Upstream Transport, Downstream Transport, Business Travel, and Employee Commute. Our assessment aligns with recognized global frameworks such as the GHG Protocol, ensuring our analysis is robust and reliable.
This analysis has identified the underlying causes and potential mitigation measures for our Scope 3 emissions. As a result, we are now better positioned to develop strategic goals for reducing these emissions. These goals are being discussed internally and will be published in the coming financial year (FY24).

By building resilience, we prioritize protecting our business and stakeholders against external threats and shocks. To achieve this, we have launched strategic initiatives to gain a comprehensive understanding of how climate change affects our business and enhance our ability to withstand external shocks.
Our initiatives align with leading international frameworks and guidelines, such as the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosure (TCFD) and the CDP. We are conducting physical and transition scenario analysis using the TCFD recommendations, Scope 3 inventorization, and developing a comprehensive decarbonization plan as part of these efforts.
We consider these initiatives crucial to our overall business strategy and have our Board of Directors oversee climate strategy initiatives. The Board regularly reviews progress against these initiatives in dedicated meetings focusing on climate-related issues. Our CFO leads the ESG Core Committee, which comprises key internal stakeholders and senior management. The committee implements climate-related measures within the organization and provides direct management supervision on key climate-related issues. Our Board of Directors and ESG Core Committee are trained bi-annually on climate-related issues and risks.
The Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosure (TCFD), its recommendations, and strategies are crucial for companies to manage climate-related risks and opportunities. Lupin’s TCFD methodology is grounded in rigorous climate risk studies, GHG inventorization, and analysis of existing institutional arrangements.
Our TCFD report, which is published independently, covers all four key pillars: Governance, Strategy, Risk Management, Metrics, and Targets. By collecting and analyzing data based on these pillars, we can comprehensively understand climate-related risks and opportunities for our business. Our climate risk assessments consider physical and transition risks and use the outputs to draft responses under different scenarios.
Climate change poses physical risks in sudden events (acute) or long-term changes (chronic) in climate patterns, which can have financial implications for organizations. Lupin’s physical risk assessment considers two climate scenarios: SSP 2 (Middle of the Road) and SSP 5 (Fossil-fueled Development). These scenarios represent the Above 2-degree and Below 2-degree scenarios.
The assessment includes two time periods:
2020-2039 and 2040-2059. Historical reference/baseline (1995-2014) data was extracted. Anomaly (difference from the average or baseline) was calculated for various indicators such as temperature, precipitation, cooling degree days, cyclones, and water stress.
Composite climate risk index and vulnerability index were developed to assess the financial impact on Lupin’s business units. The assessment focuses on near- and mid-term periods (2020-2039, 2049-2059) as the impacts of climate change are already being experienced.
Transitioning to a lower-carbon economy requires addressing risk mitigation and adaptation requirements related to climate change through policy, legal, technology, and market changes. Lupin conducted a scenario analysis until 2050 to assess the financial and reputational risks associated with upcoming/anticipated changes in policies, regulations, markets, and technologies resulting from climate change impacts.
The assessment utilized the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) Scenarios - NDC Scenario, Below 2°C Scenario, Net Zero 2050 Scenario, Delayed Transition Scenario, and Divergent Net Zero Scenario, which differentiate transition pathways based on long-term temperature targets, net-zero targets, short-term policy, overall policy coordination, and technology availability.
By implementing TCFD guidelines, we provide stakeholders with a confident analysis of our climate-related risks and opportunities. Leveraging the core elements of TCFD, we offer reliable and informed investment, credit, and insurance underwriting decisions critical for managing climate-related risks and opportunities effectively.
Under SSP 2 scenario, Vadodara and Kalpataru (Mumbai) sites will be most impacted by climate hazards by 2060. Under SSP 5 scenario, Vadodara, Kalpataru (Mumbai), Aurangabad, and Mandideep sites will be most impacted by climate hazards by 2060. Both scenarios will experience an increase in consecutive wet spell days, potentially leading to localized urban flooding. Mumbai and Vadodara will face increased water stress and scarcity, affecting industrial water usage. Alternative water usage and storage strategies need to be explored. Mumbai will experience the highest rise in very hot days, which can result in heat waves impacting staff health and infrastructure. Cooling costs for product storage will increase. To mitigate this risk, more efficient cooling systems have been installed.
Based on the above-mentioned 5 NGFS scenarios (NDC scenario, Net Zero 2050, Delayed transition, Divergent Net Zero Transition, and Below 2°C scenario), the analysis for Lupin is as follows:
Lupin has taken a proactive approach to mitigating climate change. Our comprehensive decarbonization strategy enables us to have an improved understanding of our impact on the environment, and institute necessary measures to minimize it.
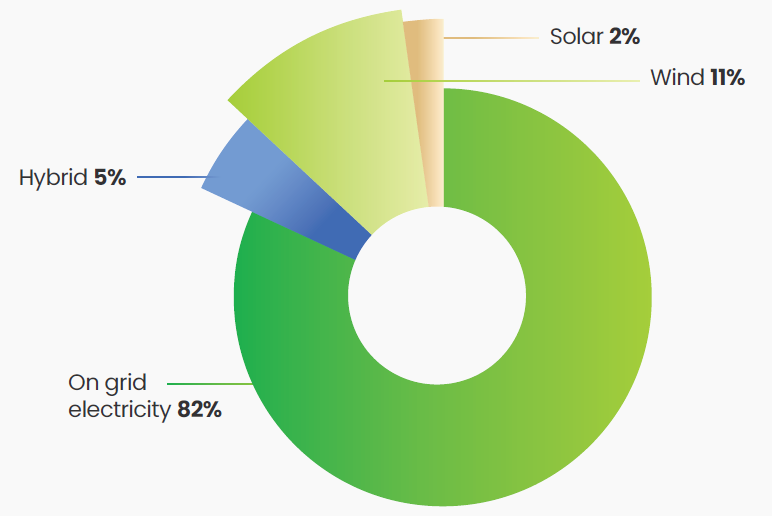
We have several ongoing initiatives, such as procuring renewable energy (Solar and Wind) through various market options and switching our boiler operations to renewable fuel sources.
In addition to this, we have also conducted a phase-wise study of all our facilities to identify any potential for further efficiency improvements. Our analysis considers geographic, economic, and social factors, to identify optimal energy source options for each site.
As an outcome of this analysis, we have transitioned our Tarapur and Pithampur sites from furnace oil to natural gas, which is less emission-intensive. While our Jammu, Goa, and Aurangabad sites have already been using cleaner fuels derived from Agro-waste.
We are also introducing Agro waste boilers as a more environmentally friendly fuel source at our Nagpur, Mandideep, Pithampur, Sikkim, Tarapur, Dabhasa & Ankleshwar.
Furthermore, by adopting a hybrid renewable power model comprising wind and solar, the contribution of renewable power at our Ankleshwar and Dabhasa sites in FY23 has increased by ~5.3 MW. While our total procurement of renewable electricity has increased to 5.37% in FY23.
109,274 metric tons CO2 (9.45 % reduction compared to FY20)
Overall Reduction in Scope 1, 2 & 3 GHG Emissions due to Decarbonization Effortsconventional
Water is crucial for our operations worldwide and is utilized in various production and packaging processes. Recognizing the significance of a reliable water source and the need to be responsible stewards, we prioritize sustainable water management. Our strategy focuses on business continuity, water risk mitigation, and conservation efforts.
We implement technical interventions like water recycling plants, reusing AHU condensate and rainwater, and adopting water-efficient mechanisms to achieve these goals. These measures help us reduce our water consumption and minimize our impact on other sectors, such as agriculture and domestic water needs.
We have taken a target of recycling 50% of our total water withdrawal in our operations by 2025. In FY23 we recovered 42% of water, which puts us on track to meet this target.


In FY22, we partnered with external consultants to conduct a baseline assessment of water risk at our manufacturing locations in India. The assessment revealed that five operating locations – Pithampur, Nagpur, Jammu, Aurangabad, and Ankleshwar – are in regions of Extreme High-Water Risk, as measured by the WRI Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas tool. This information helps us identify sites that may be exposed to Baseline Water Stress by 2030 and the ratio of total water withdrawals to available renewable surface and groundwater supplies. We continue to use this assessment to devise our water management strategies and prioritize key focus areas for optimal water management.
Lupin Foundation undertakes water stewardship activities at Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh. We have been able to create water recharge potential of the order of 400% of our total water withdrawn, thereby making an overall water-positive impact.
Lupin is committed to minimizing negative impacts in all aspects of our operations, including our water discharge practices. We recognize the potential harm water discharge from manufacturing sites can cause communities and the environment. We have implemented technologies and systems to achieve Zero Liquid Discharge at six manufacturing sites to address this. This ensures that effluents from our processes are not discharged into water bodies through run-offs. We are also working towards certifying our remaining sites as Zero Liquid Discharge facilities.
Further, at nine of our sites in India, after primary treatment, the wastewater is further processed in state-of-the-art water recovery plants consisting of Reverse Osmosis (RO), Multiple Effect Evaporator (MEE), and Agitated Thin Film Dryer (ATFD) plants to recover water from the wastewater efficiently. The recovered water is then redirected for other internal uses.
Lupin recognizes the importance of Anti-Microbial Resistance (AMR) stewardship in our sustainability strategy, as it directly impacts human and ecological well-being.
AMR poses a significant threat to public health by reducing the effectiveness of antibiotics and other anti-microbial drugs. The excessive use and improper disposal of these drugs can lead to contamination of water bodies, soil, and food chains, aggravating the problem further. This contamination disrupts the natural balance of ecosystems and their overall functionality.
Therefore, in response to the AMR challenge, Lupin focuses on three of the four key areas: appropriate antibiotic use, access, and environmental impact.
Lupin incorporates efficient waste management and circularity practices across our entire value chain. This involves conscious inventory/purchase management, employing long-lasting chemical products, and utilizing equipment that generates minimal hazardous waste. Our employees receive training in safely handling, labeling, and storing hazardous products.
We take non-hazardous waste from our operations, such as canteen and mycelia, and send it to piggeries or composters to convert into usable organic fertilizer. In FY23, we successfully sent 5,713 MT of canteen and mycelia waste and 1,265 MT of agro-waste boiler to their respective destinations. Agro-waste boiler ash is also utilized for brick manufacturing, soil enrichment, and landfilling. There is no other means of waste disposal adopted by Lupin, apart from ones mentioned below:


We take our commitment to responsible waste management seriously. That’s why we prioritize waste recycling and reducing landfill and incineration. Seven of our thirteen sites, including R&D, send incinerable hazardous waste to Co-processors/Pre-processors. In March 2023, we received permission to dispose off incinerable hazardous waste to the pre-processor for the Tarapur site.
In FY23, we sent 4,175.21 MT (60.9%) of incinerable hazardous waste for co-processing, an increase from 3,099.3 MT (44.5%) in FY22. It indicates that we have already achieved the 60% target aimed for 2025 in FY23.
Moreover, as our global API sales continue to increase yearly, we recognize our responsibility to implement and enhance processes that help recover, reuse, and recycle spent solvents generated from the API manufacturing process. We also ensure that spent or used oil generated from our operations is sent to authorized recyclers or registered disposal facilities.
Finally, as part of our resource conservation initiatives, we sent 4,452 MT of spent calcium sulfate to cement plants for utilization as raw material in their operations.
We are fully committed to our Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) obligations, ensuring the efficient recovery of post-consumer plastic waste from our products in India. This waste is either recycled or used as an alternative energy source. In addition, we have digitized all our consumer and patient information leaflets, reducing both costs and paper consumption.
In FY23, we achieved our EPR target with 100% completion, collecting and channelizing, 1,956 MT of plastic waste to processors.

